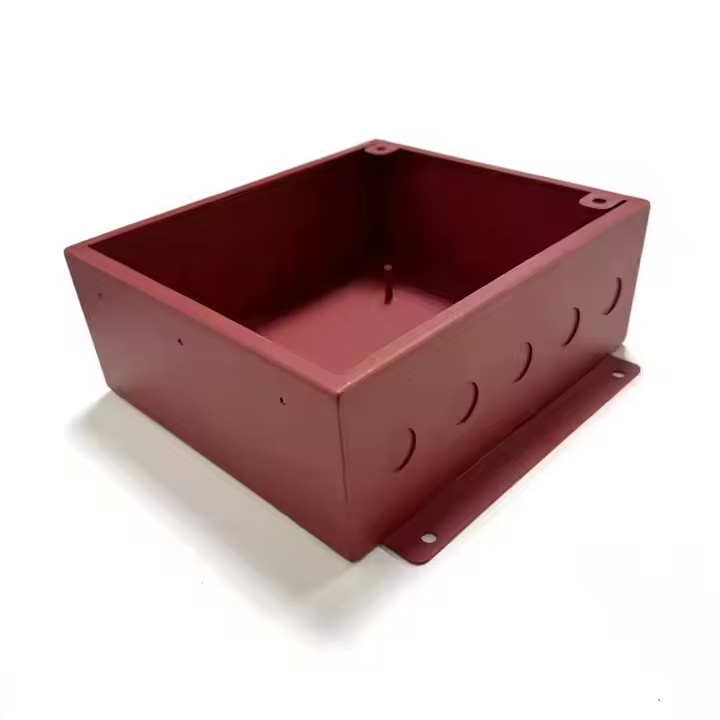
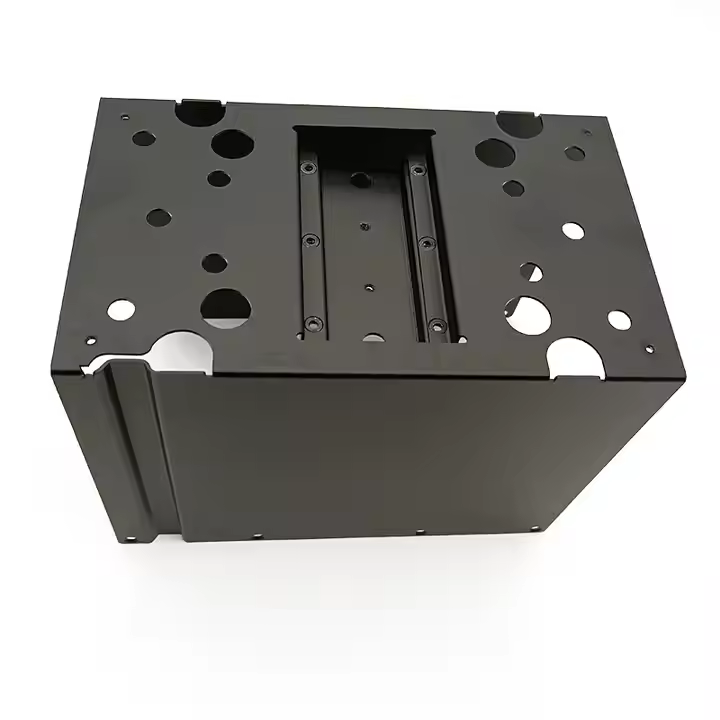
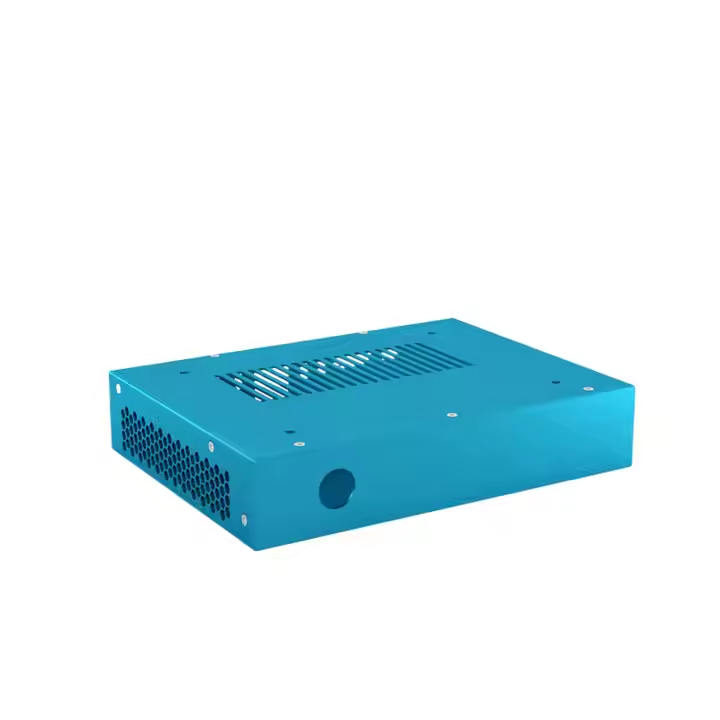
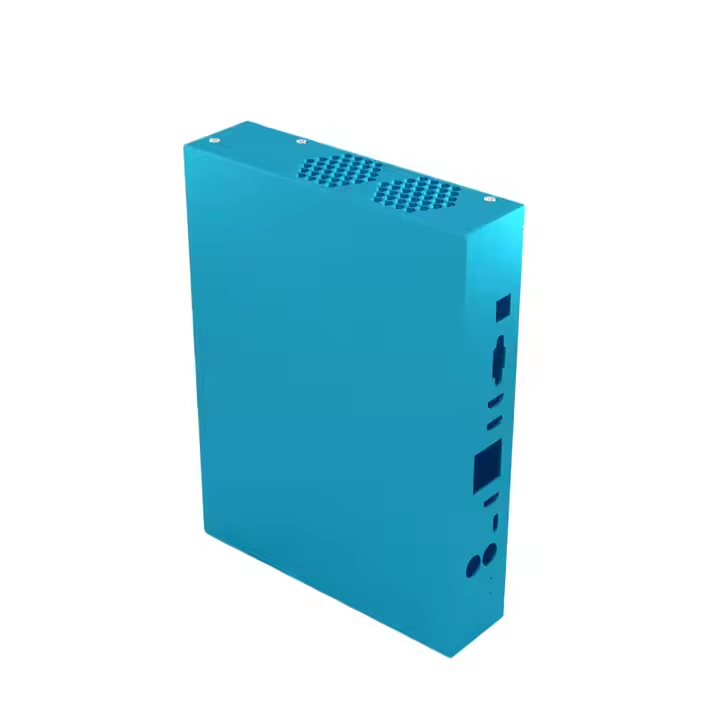
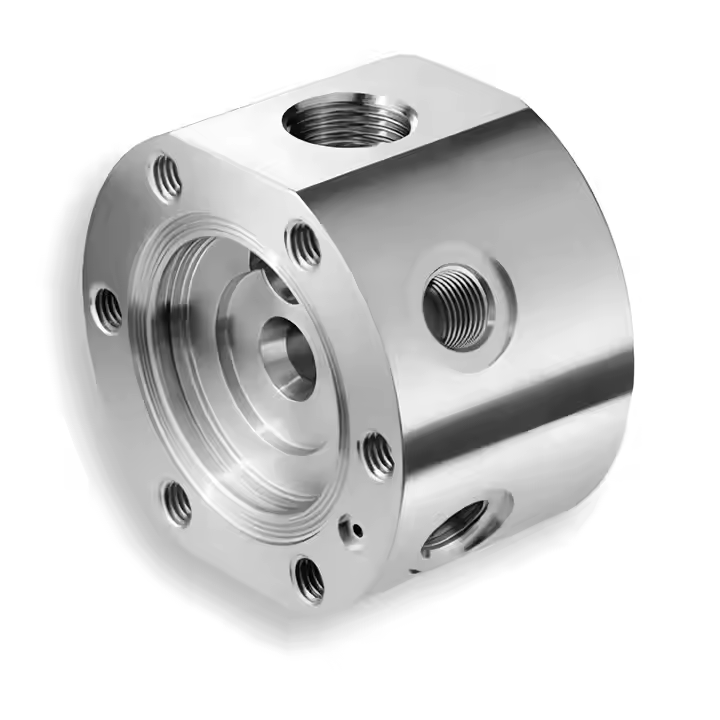
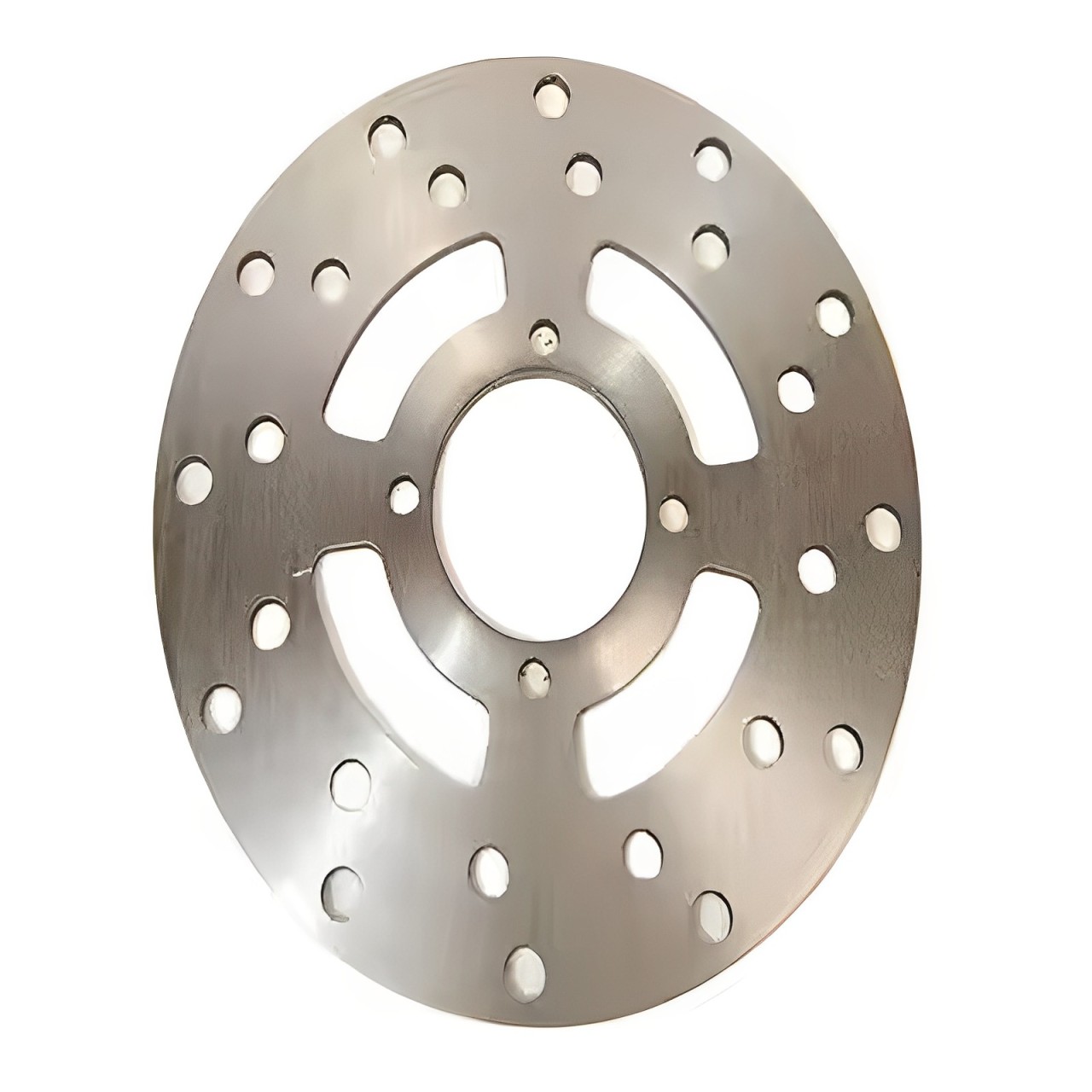
Product Description
Welding is a manufacturing process that joins materials, typically metals or thermoplastics, by using heat, pressure, or both. The process causes the material to melt and fuse together. Common types of welding include:
- Arc Welding: Uses an electric arc to melt the workpiece and filler material (e.g., MIG, TIG, Stick welding).
- Gas Welding: Uses a flame from burning gas (e.g., Oxy-acetylene welding).
- Resistance Welding: Joins materials by applying heat generated from electrical resistance (e.g., Spot welding).
- Laser Welding: Uses laser beams for precise and deep penetration.
Welding can be done manually or with automated machinery, and it's widely used in industries like construction, automotive, and manufacturing. Proper safety measures are crucial due to high temperatures, sparks, and potential exposure to hazardous fumes.
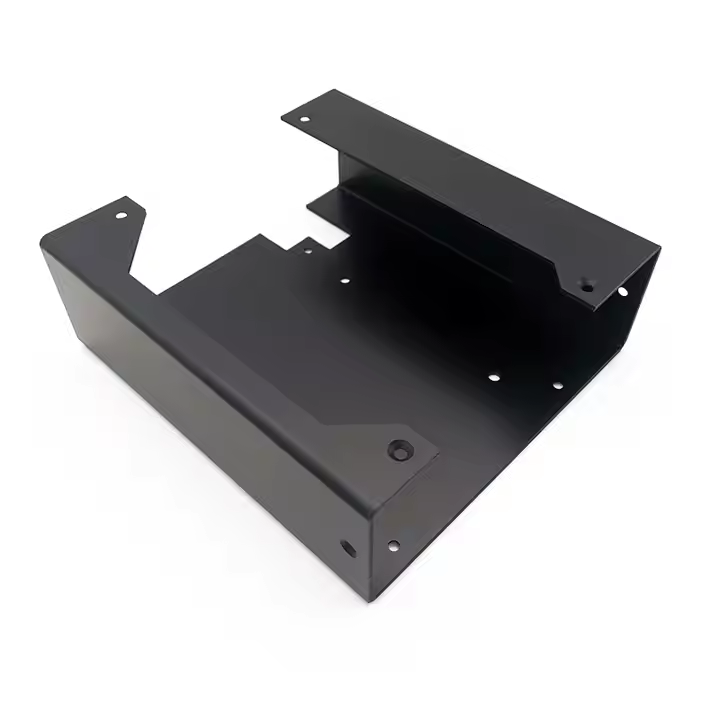
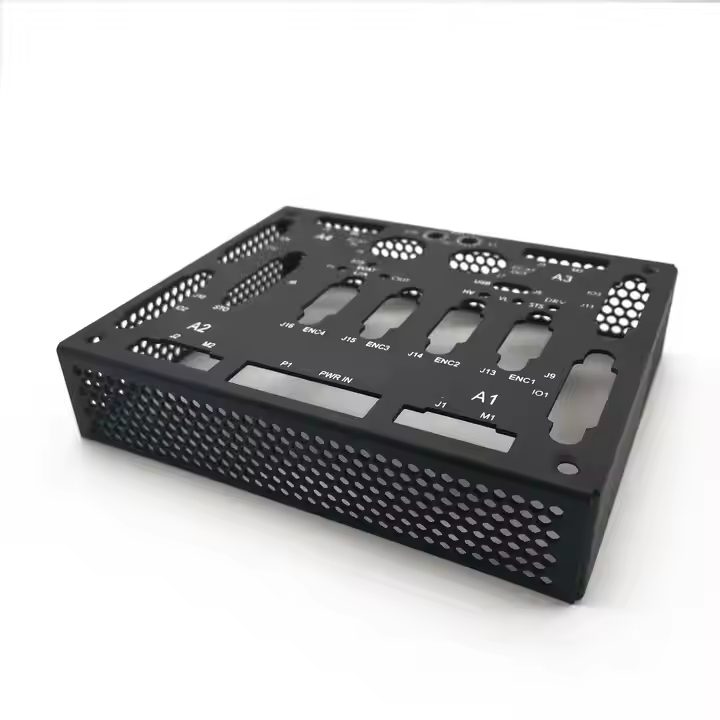
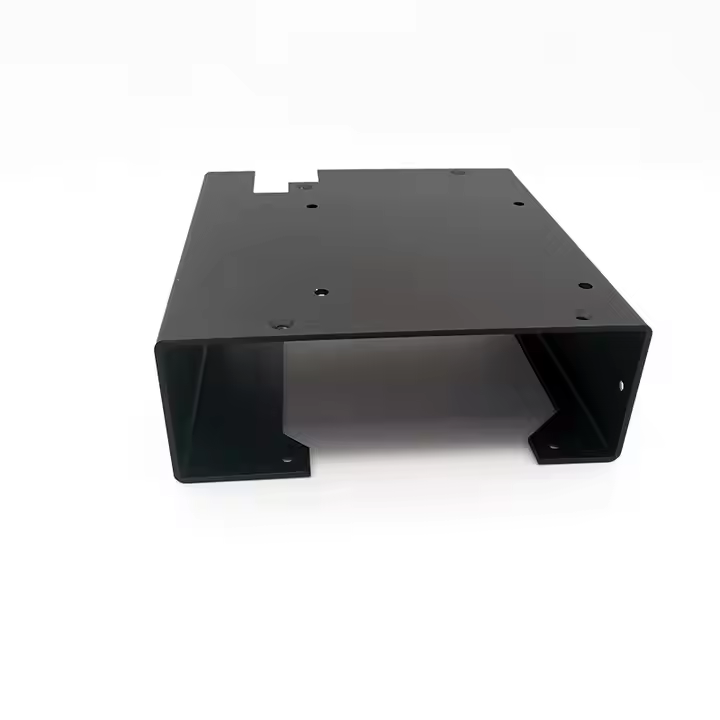



Product parameters
| List | Details |
|---|---|
| Brand Name | Welding part |
| Color | Customized Colors |
| OEM/ODM | OEM ODM CNC Milling Turning Machining Service |
| MOQ | Small Orders Accepted |
| Service | Customized OEM CNC Machining |
| Application | Industrial Equipment |
| Equipment | CNC Machining Centres |
| Material | Stainless Steel |
Custom Process

Design and Programming
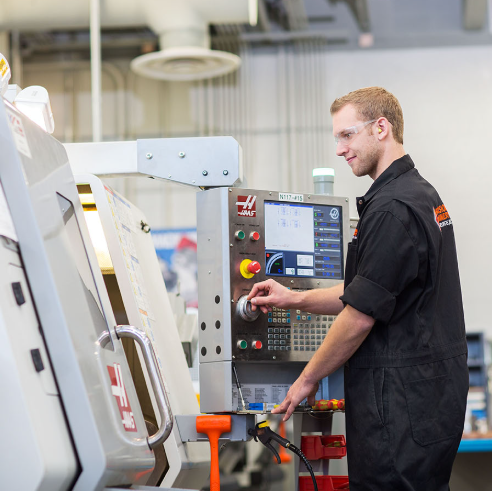

Machine Setup
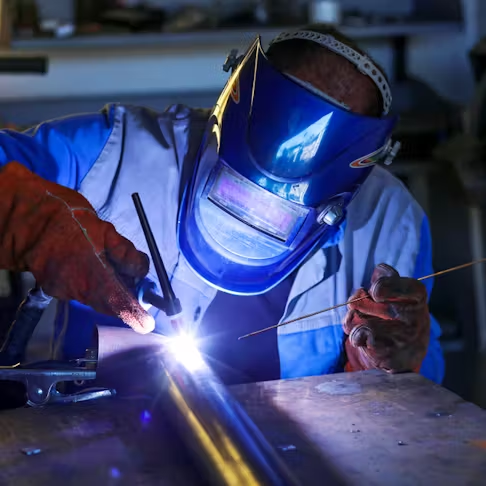

Welding Process Execution
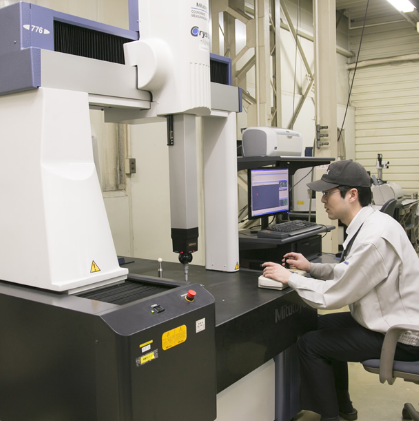

Inspection and Finishing
Process Type

Solid State Welding

Newer Welding

Gas Welding
Material

Brass

Copper

Aluminum

Metal
Quality Control
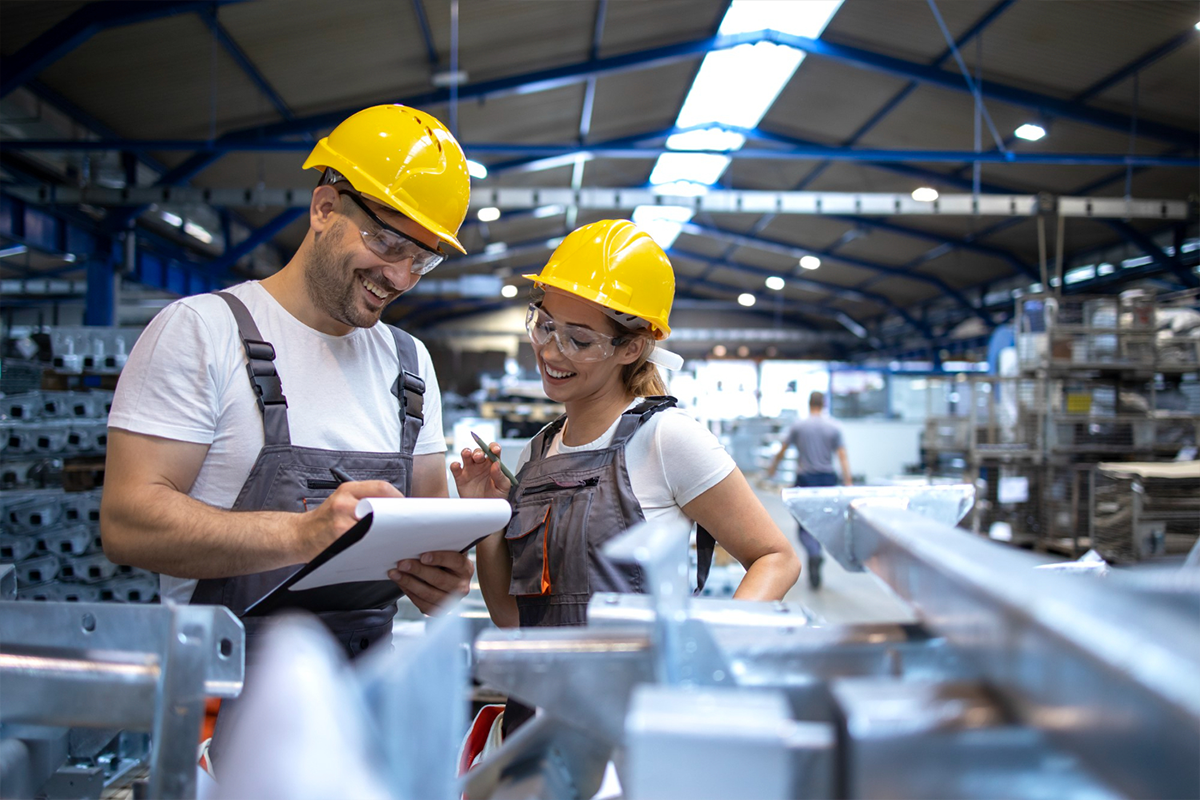

CNC welding is a highly precise and efficient process that combines computer control with advanced welding technology to produce high-quality welds with minimal human intervention. By automating the welding process, CNC welding offers numerous advantages, including enhanced precision, repeatability, and the ability to perform complex welds for various materials and industries.
The quality control (QC) process in CNC welding is crucial to ensuring that welded parts meet stringent standards. It involves careful pre-welding checks, real-time monitoring during the welding process, and comprehensive post-welding inspections, including non-destructive testing and dimensional checks. Adhering to established standards like ISO, AWS, and ASME ensures that welds are structurally sound and reliable.
Ultimately, CNC welding, supported by rigorous quality control practices, plays a key role in improving productivity, reducing errors, and delivering consistently high-quality welded products across diverse industries, from automotive to aerospace to manufacturing.
Processing capability

The processing capability of welding refers to the range of materials, thicknesses, precision, and speed that different welding processes can handle. Common processes include MIG, TIG, Stick, FCAW, and SAW, each with unique strengths suited to specific applications. For instance, TIG welding offers high precision, making it ideal for thin materials and critical applications like aerospace, while MIG welding is faster, suited for high-volume production of thicker materials. Laser welding and electron beam welding offer extremely precise, low-heat solutions for specialized industries, while SAW excels in heavy-duty, thick materials with deep penetration.
Additional processes
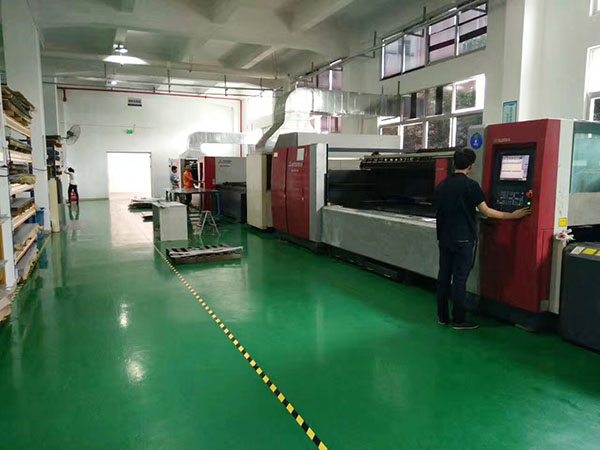

Welding processes can also vary in their heat-affected zones (HAZ), speed, and post-weld treatment requirements. Automated CNC welding enhances precision and repeatability, especially for complex welds. Ultimately, the choice of welding method depends on factors like material type, joint design, required quality, and production volume. Quality control is critical to ensure weld strength and reliability across all processes.
4o mini