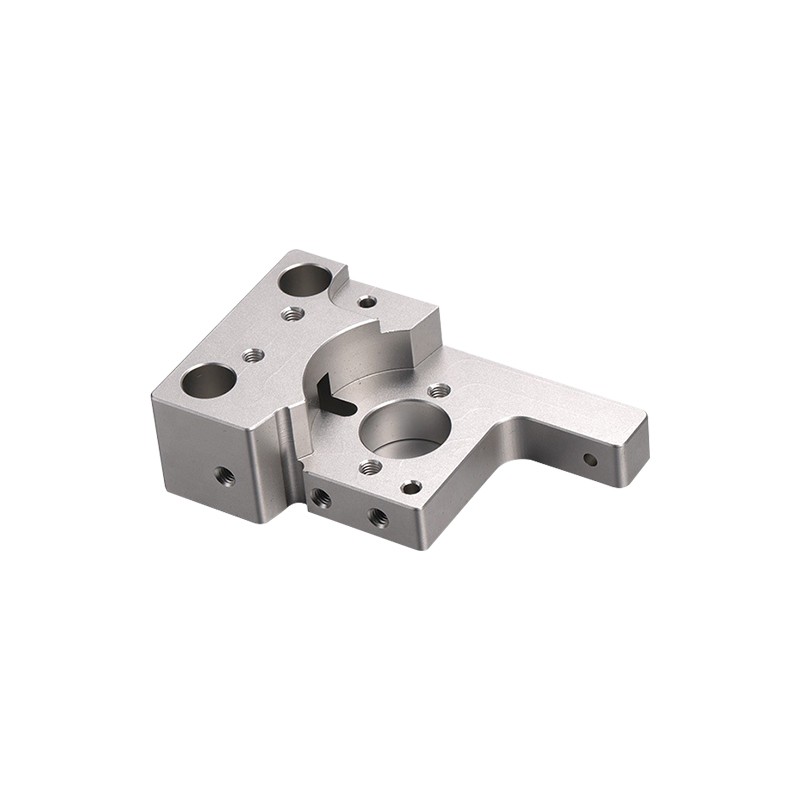
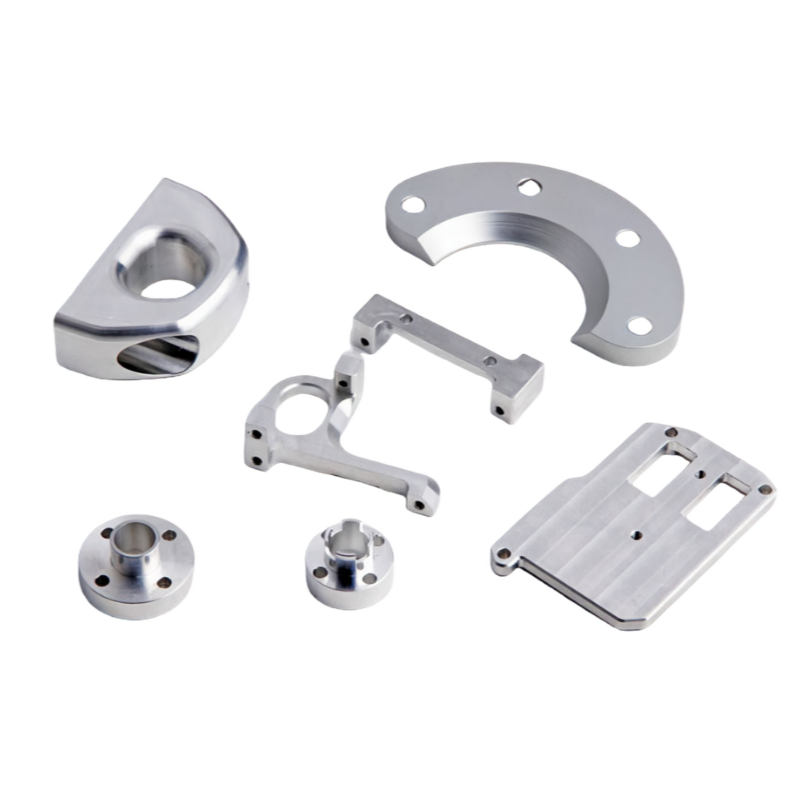
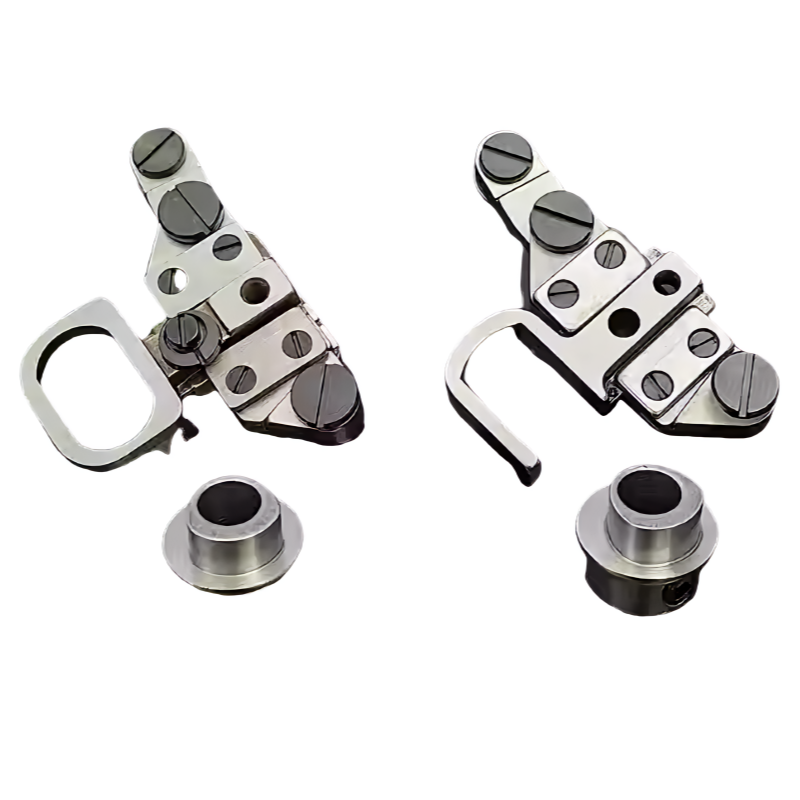
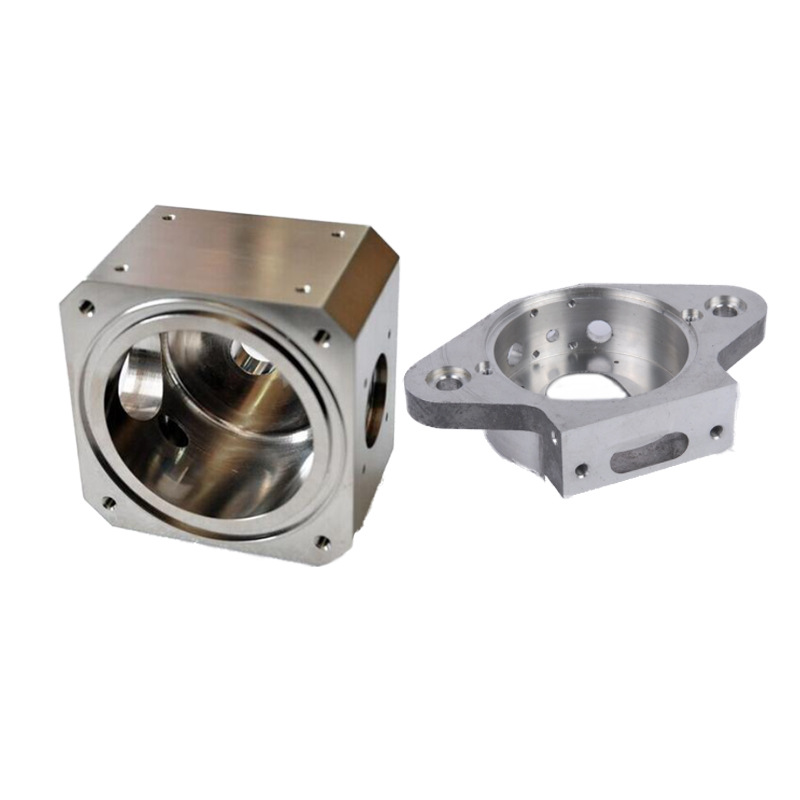
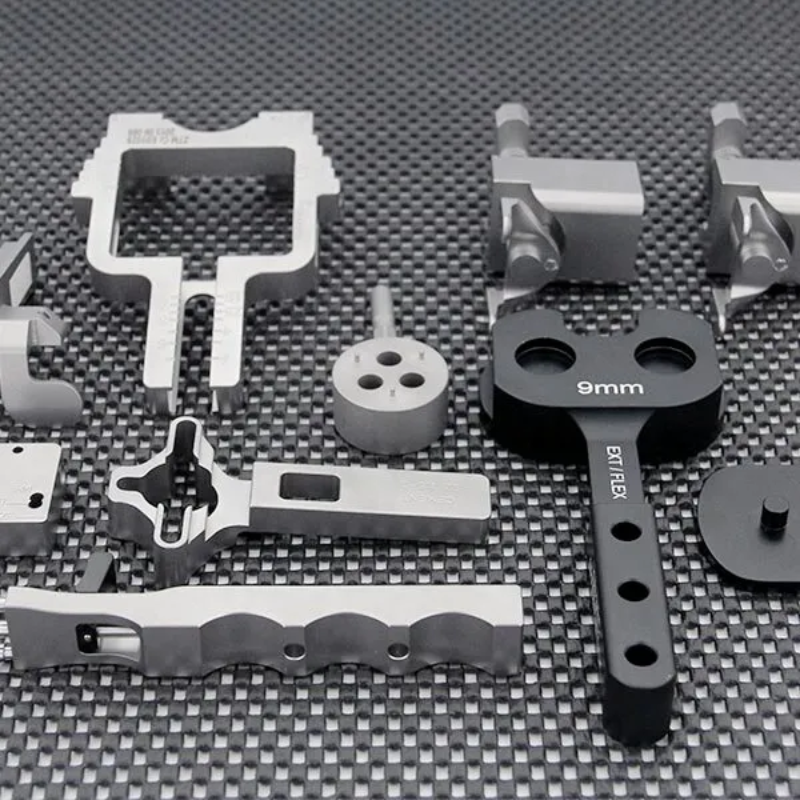
Product Description
CNC precision parts are crucial in a wide range of industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, electronics, defense, and manufacturing, where even the smallest deviation from the specified dimensions can result in failure. From prototyping to large-scale production, CNC machining offers the flexibility to create complex geometries and custom designs that meet the highest standards of quality and performance.



Product parameters
| Software/format | PRO/E, Auto CAD, Solid works, IGS, UG, CAD/CAM/CAE |
| Tolerance | 0.01~0.05mm, can customize as per request. |
| Dimension | Customized, MAX OD 300*300MM |
| Test equipment | Measurement instrument, projector, CMM, Altimeter, Micrometer, Thread Gauges, Calipers, Pin gauge etc. |
| Production Equipment | CNC Machining lathe, Hot forging & Hydraulic compress machine, Auto-milling machine, Drilling and Milling Center, Braid machine |
| Material | Aluminium, Brass, Bronze, Stainless steel and Steel as well as Plastics. |
| Surface Treatment | Zinc/Nickel/Chrome Plating, Passivation, Hardening, Clear Anodizing, Black Anodizing, Black Oxide, Coating, Degreasing, Brushing, Electronic |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 ISO 13485 Compliance Statistical Process Control (SPC) 5S |
| Packing | Inner packing: Plastic/paper wrap, bubble bag, PE foam, EPE cotton, PPbag Custom made Outer packing: carton box, steel pallet etc. |
Custom Process

1. Inquiry

2. Negotiation
3. Payment Term
4. Machining Production

5. Inspection samples
6. Package

7.Transportation
8. After-sale support
Process Type
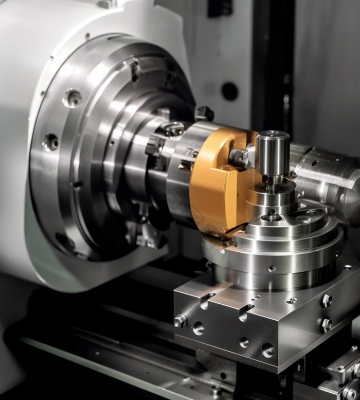
Turning
CNC machining process where a rotating workpiece is shaped using a stationary cutting tool that removes material to create precise geometries, typically cylindrical or conical in form. The workpiece is securely held on a CNC lathe, which spins at high speeds while the cutting tool moves along its length to achieve the desired shape, diameter, or surface finish. This process is ideal for producing parts like shafts, rings, and threaded components with high accuracy. Various turning operations such as straight turning, taper turning, and thread cutting are employed, depending on the specific design requirements. CNC turning offers exceptional precision, repeatability, and efficiency, making it essential for producing both simple and complex components across industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical.

Milling
CNC machining process where a rotating cutting tool is used to remove material from a stationary workpiece, typically to create flat, contoured, or complex shapes. The workpiece is mounted on a CNC milling machine, which moves in multiple axes (usually X, Y, and Z) to precisely position the cutting tool. Milling operations can include a variety of techniques such as face milling, end milling, and slot milling, which allow for the creation of features like holes, pockets, grooves, and intricate surface details. The process is highly versatile and can be used on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, making it ideal for producing both simple and complex parts with high accuracy and fine surface finishes. CNC milling is essential in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where precision and flexibility are key.

Machining
Broad term that refers to a range of processes used to shape, cut, or remove material from a workpiece to achieve a desired form, size, or surface finish. These processes include turning, milling, drilling, grinding, and more, and are typically carried out using computer numerical control (CNC) machines for high precision and automation. Machining processes are employed to produce complex parts with tight tolerances, such as gears, shafts, and custom components, across industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical. By utilizing various cutting tools and techniques, machining can handle a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, and is essential for both prototype and production runs, ensuring high-quality, functional parts with exacting specifications.
Material

Aluminum

Brass

Stainless Steel

Plastics
Additional processes

Grinding
- Types: Surface grinding, cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding.
- Purpose: To refine the part surface, achieve tighter tolerances, and improve surface finishes that machining alone cannot achieve.
- Common Uses: Finishing of hardened materials, precise dimensioning of parts, smoothing out rough surfaces.

Honing
- Purpose: To improve surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Typically used after boring or grinding to achieve smoother finishes.
- Common Uses: Engine blocks, hydraulic cylinders, and other parts requiring precise bore sizes and finishes.