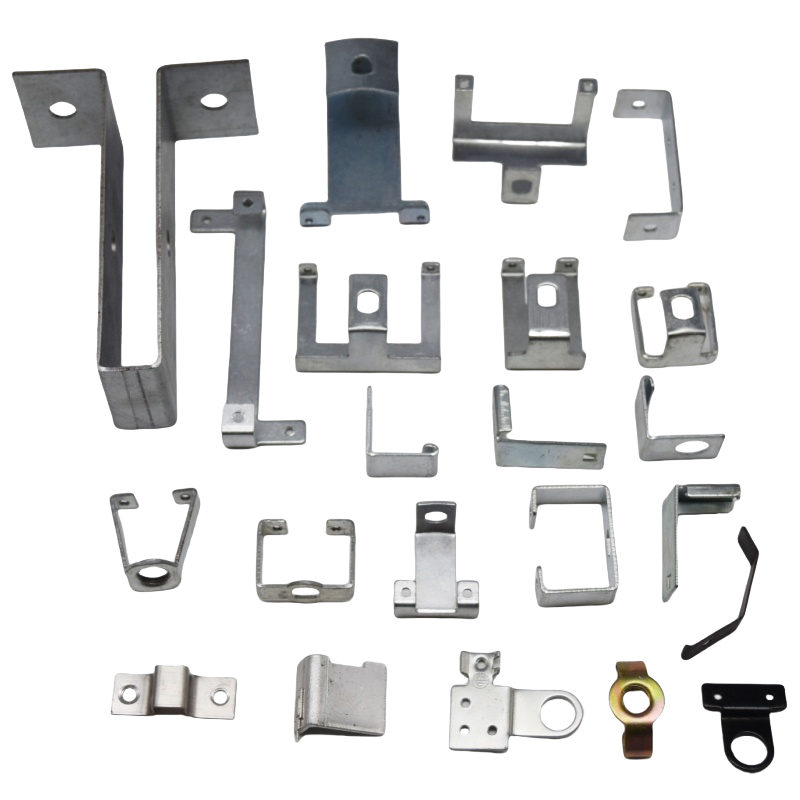
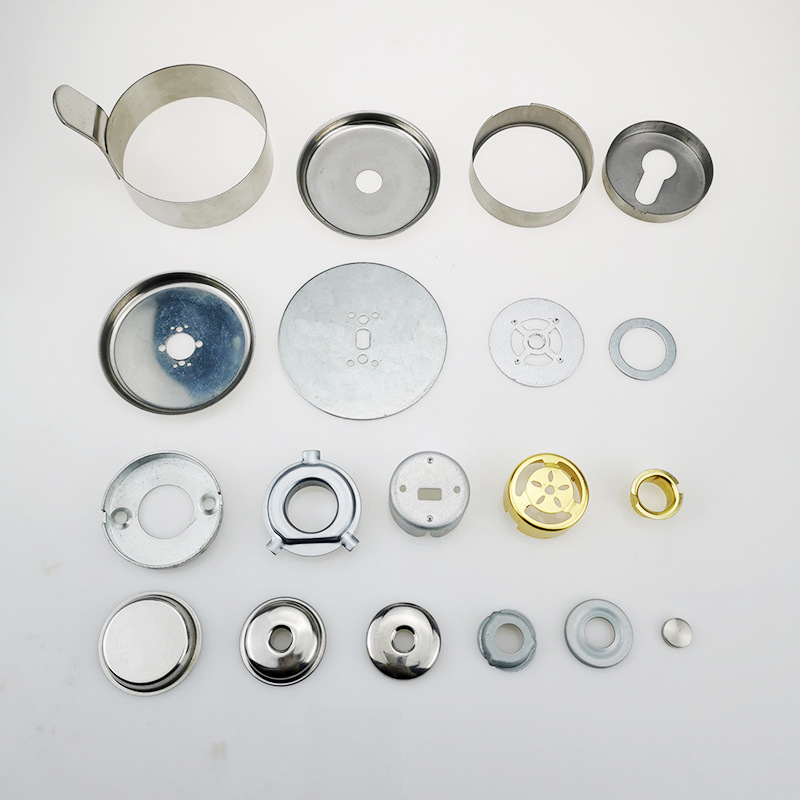
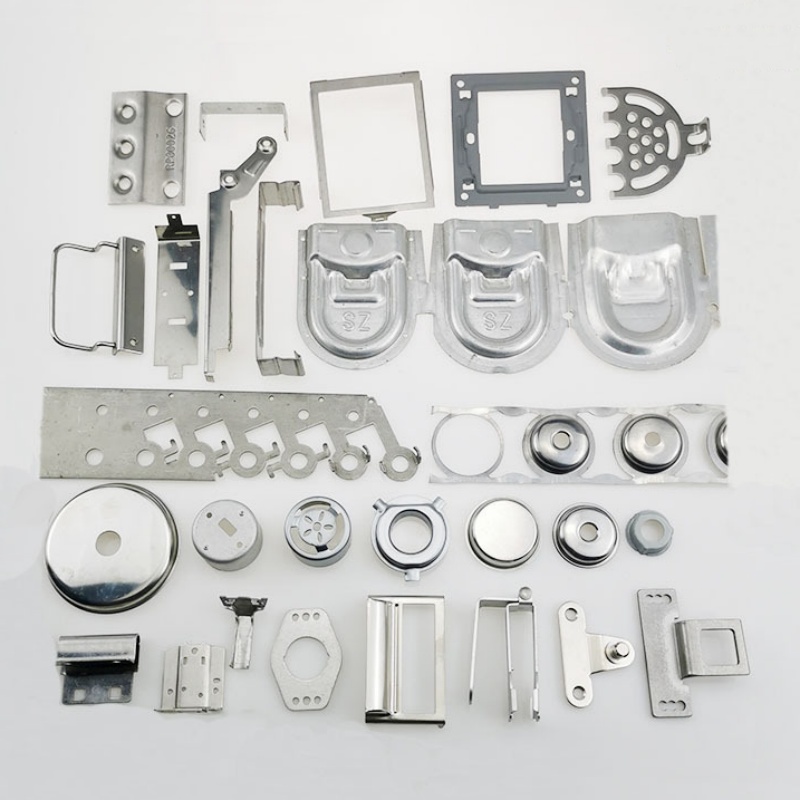
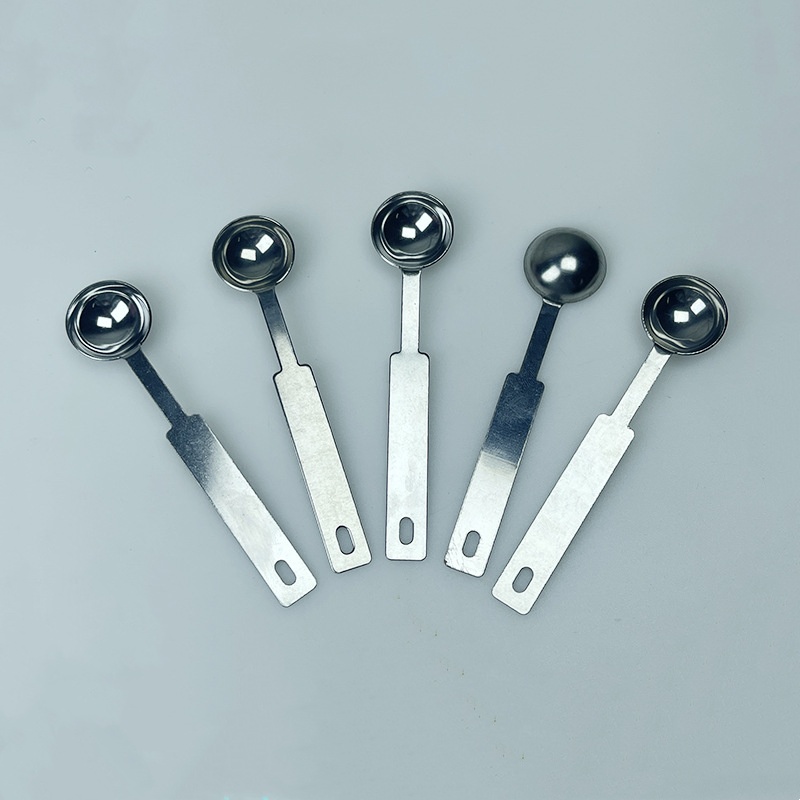
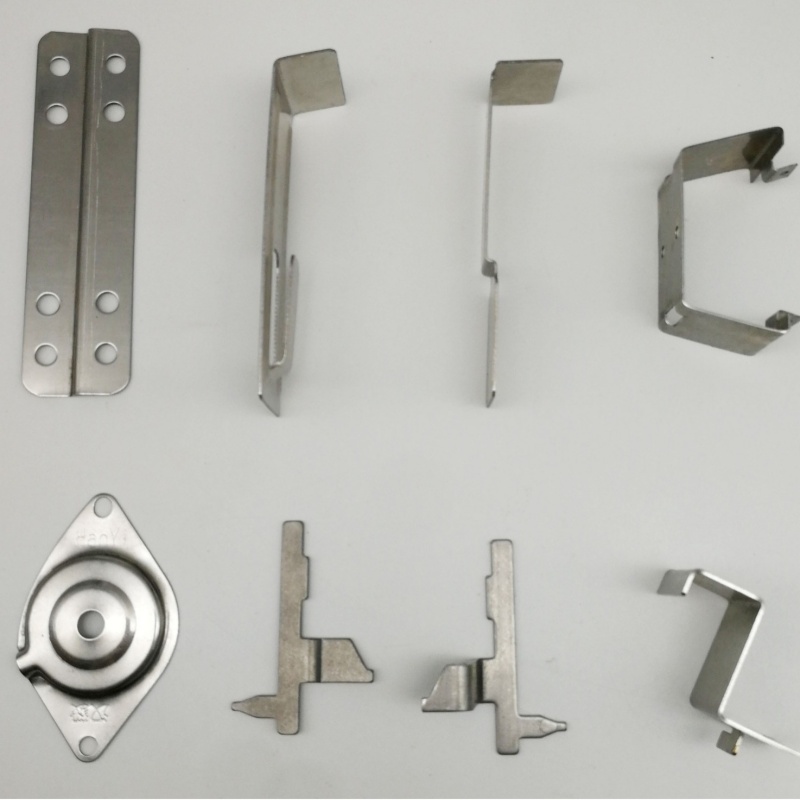
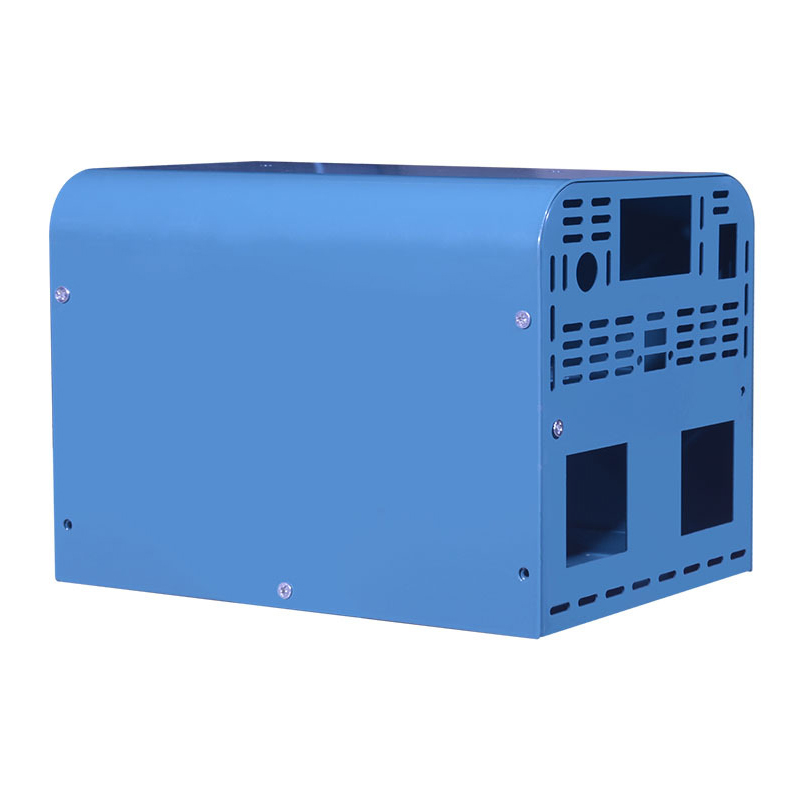
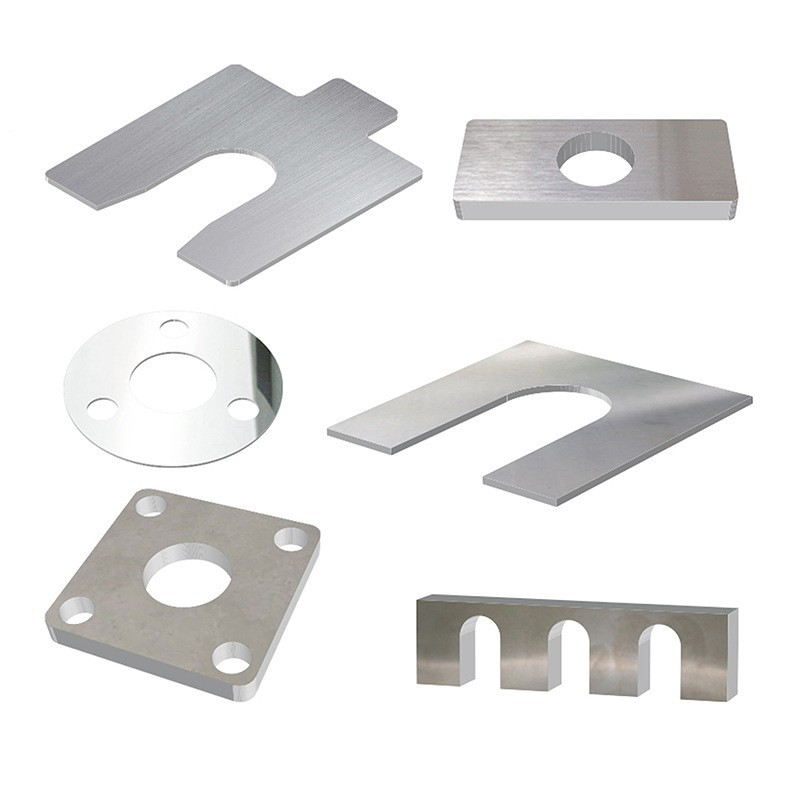
Product Description
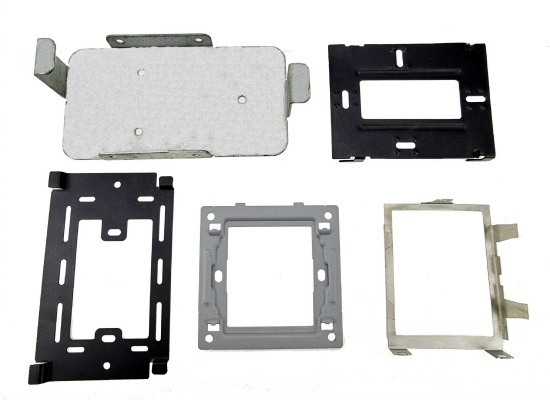

Stamping is a processing method that uses dies and presses to apply external force to plates, strips, tubes, etc., causing them to undergo plastic deformation or separation, thereby obtaining workpieces of the required shape and size.
Application
Stamping products have the advantages of high precision, high consistency, high efficiency and low cost, and are widely used in automobile manufacturing, electronic appliances, hardware products, aerospace, medical equipment and other fields.

Notebook

Optical lens mold

Automobile frame

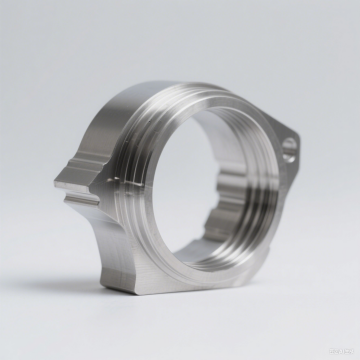
Artificial joint

Heat sink

Turbine disc
Product parameters
Processing type | Metal forming |
Mold | Multi-process continuous mold |
Minimum quantity | 1000pcs |
Material | Stainless steel, carbon steel, galvanized steel, laminated metal, sandwich material aluminum-plastic plate, aluminum alloy, titanium alloy, copper alloy etc |
Stamping process | Material preparation, mold design and manufacturing, processing equipment, post-processing equipment, inspection methods |
Custom Process

1. Send inquiries

2. Drawing or samples

3. Quotation

4. Customer confirmation

5. Places order and pays

6. Mass production

7. Test before packing

8. Shipping & confirmation
Material
Stainless steel

Carbon steel

Galvanized steel

Aluminum alloy

Titanium alloy

Copper alloy
Material preparation before processing

Material selection
Choose metal sheets based on product requirements, taking into account thickness, strength, ductility, etc.

Uncoiling and shearing
The coil material is uncoiled through the uncoiler and shears into sheet or strip materials of the required size.

Surface treatment
Cleaning or oiling (to reduce friction during stamping).
Mold design and processing
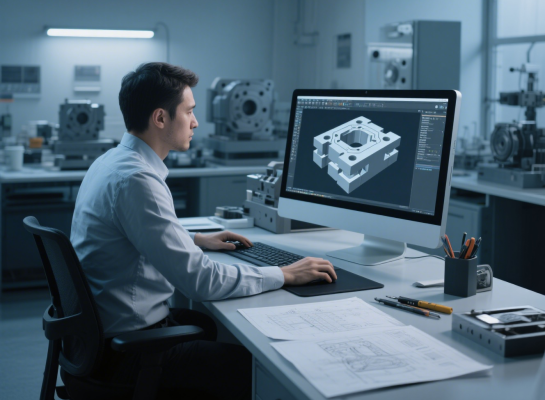

Mold design
According to the shape of the workpiece, design the punch, die, blank holder and other structures, and take into account springback, clearance, guidance, etc.
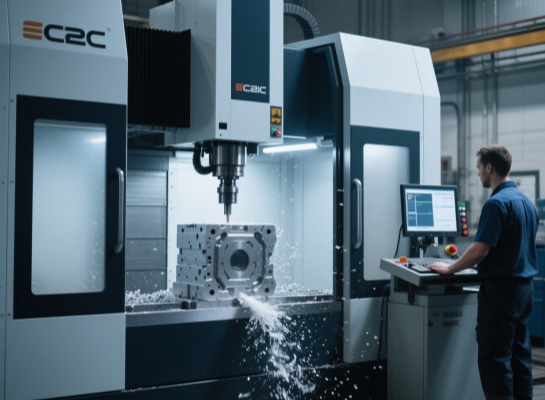

Mold processing
High-precision molds are manufactured through processes such as CNC, wire cutting, and heat treatment.
Stamping machining Equipments
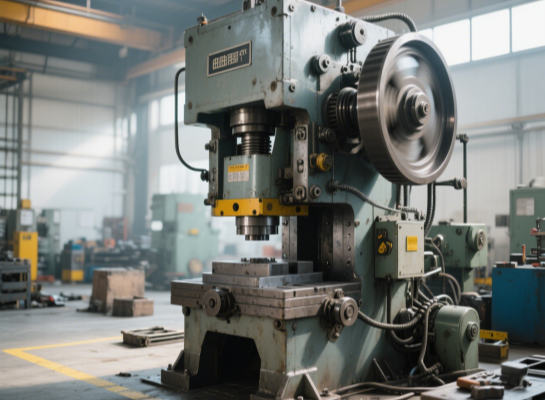

Crank press (core model)
Closed type (gantry type) : 300-2500 tons, specifically designed for automotive body panels
Double-action type: Outer slider blank pressing + inner slider stretching, essential for deep drawing process
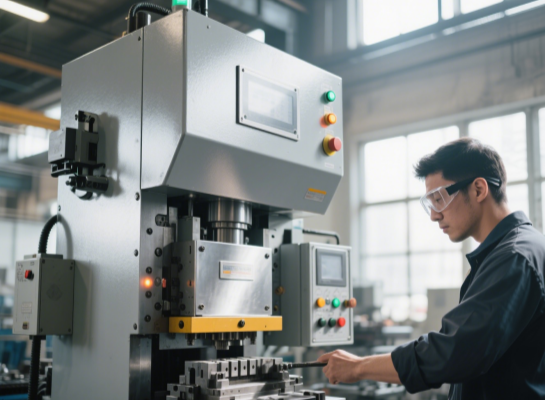

High-speed precision punch press
Typical parameters: 300 tons /800 times/minute, repeatability accuracy ±0.01mm
Innovative technology: Linear guides replace roller guides (Vibration reduced by 40%)
Hydraulic press (preferred for large tonnage)
Four-column type: 1,000-10,000 tons, with strong versatility
Frame type: Rigidity is increased by 30%, suitable for asymmetrical parts
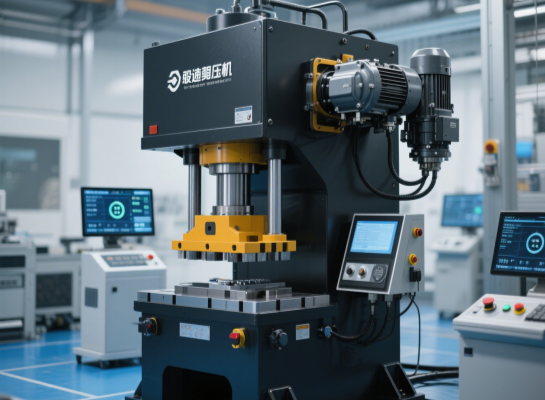

Servo direct drive press
Advantages: Programmable motion curves (e.g., slow forming → fast return stroke)
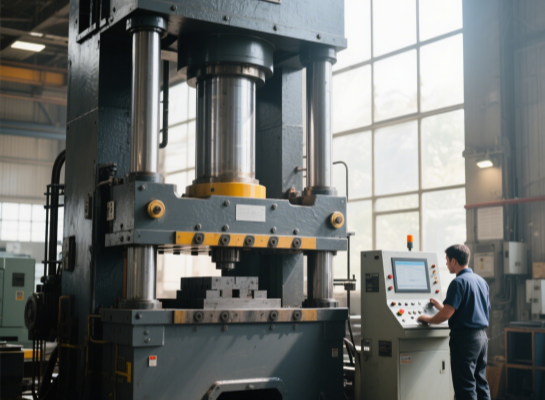

Selection of stamping equipment
Mechanical press: Suitable for high-speed stamping (such as small and medium-sized parts).
Hydraulic press: Suitable for deep drawing or large tonnage requirements.
Servo press: High precision, capable of controlling the movement curve of the slider.
Post-processing of stamping

Deburring
Remove burrs from the edges of the stamping.

Heat treatment
To increase hardness or eliminate internal stress (such as annealing, quenching).

Surface treatment
Electroplating, spraying, anodizing, etc.
Detection equipment
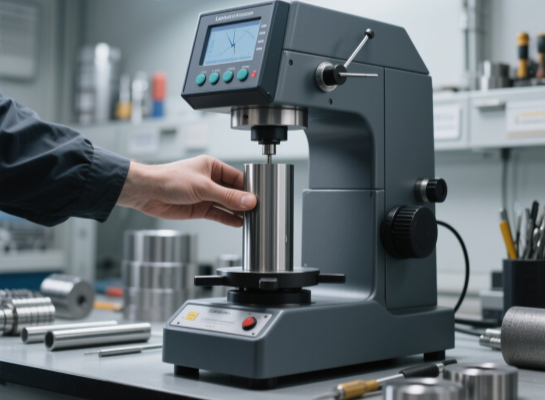

Hardness tester (Rockwell/Vickers)
Test item: Whether the hardness of the material after stamping meets the standard (such as aluminum alloy parts).
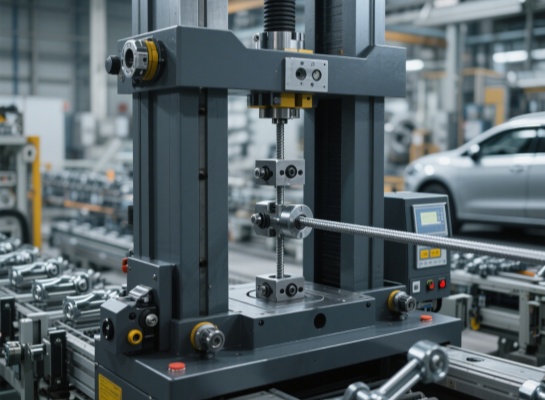

Tensile testing machine
Test items: Tensile strength, elongation (to verify whether the material becomes brittle due to stamping).

Three-coordinate Measuring machine (CMM)
Principle: By contacting the surface of the workpiece with a probe, three-dimensional coordinate data is obtained and compared with the CAD model.
Application: High-precision detection of complex surfaces, hole positions, contours, etc. (such as automotive body panels).
Advantages: High precision (micron level), capable of measuring geometric tolerances (flatness, positional accuracy, etc.).
Limitations: Slow speed, requires professional operation.

Image measuring instrument (optical measurement)
Principle: Measure two-dimensional dimensions by using high-resolution cameras and image processing technology.
Application: Thin plate parts, small hole diameter, edge distance, etc. (such as electronic hardware parts).
Advantages: Non-contact and rapid measurement of planar dimensions.
Limitation: Sensitive to reflective or transparent surfaces.

Surface defect detector
Principle: By integrating high-brightness light sources with industrial cameras, AI algorithms are used to identify scratches, indentations, rust spots, etc.
Application: Stamping parts with strict appearance requirements (such as home appliance panels).
Advantages: Fully automated inspection, real-time alarm.
Expansion: It can be used in conjunction with a colorimeter to detect the uniformity of the coating.





















