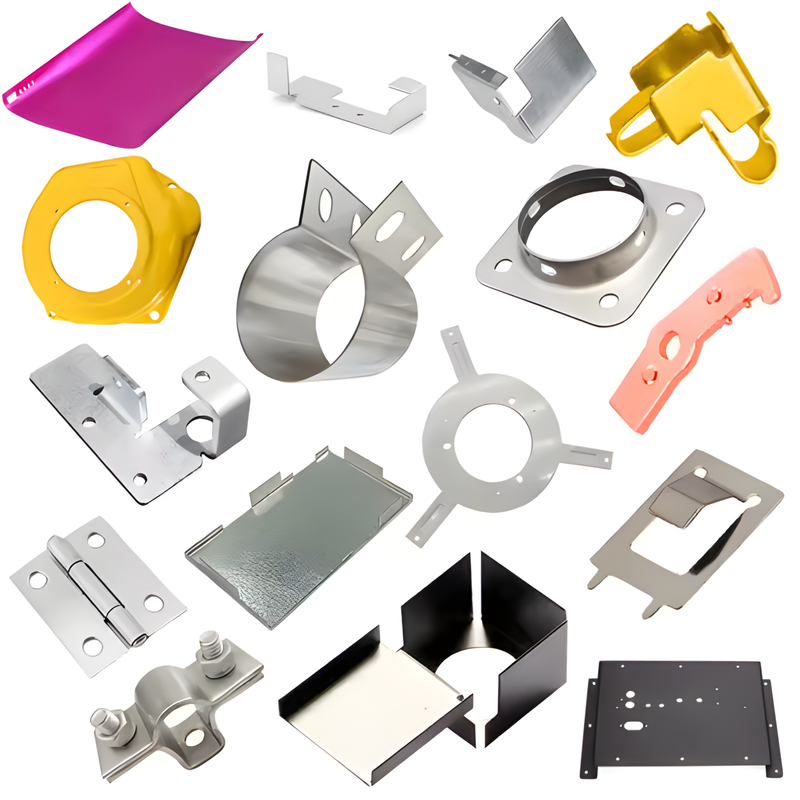
Product Description
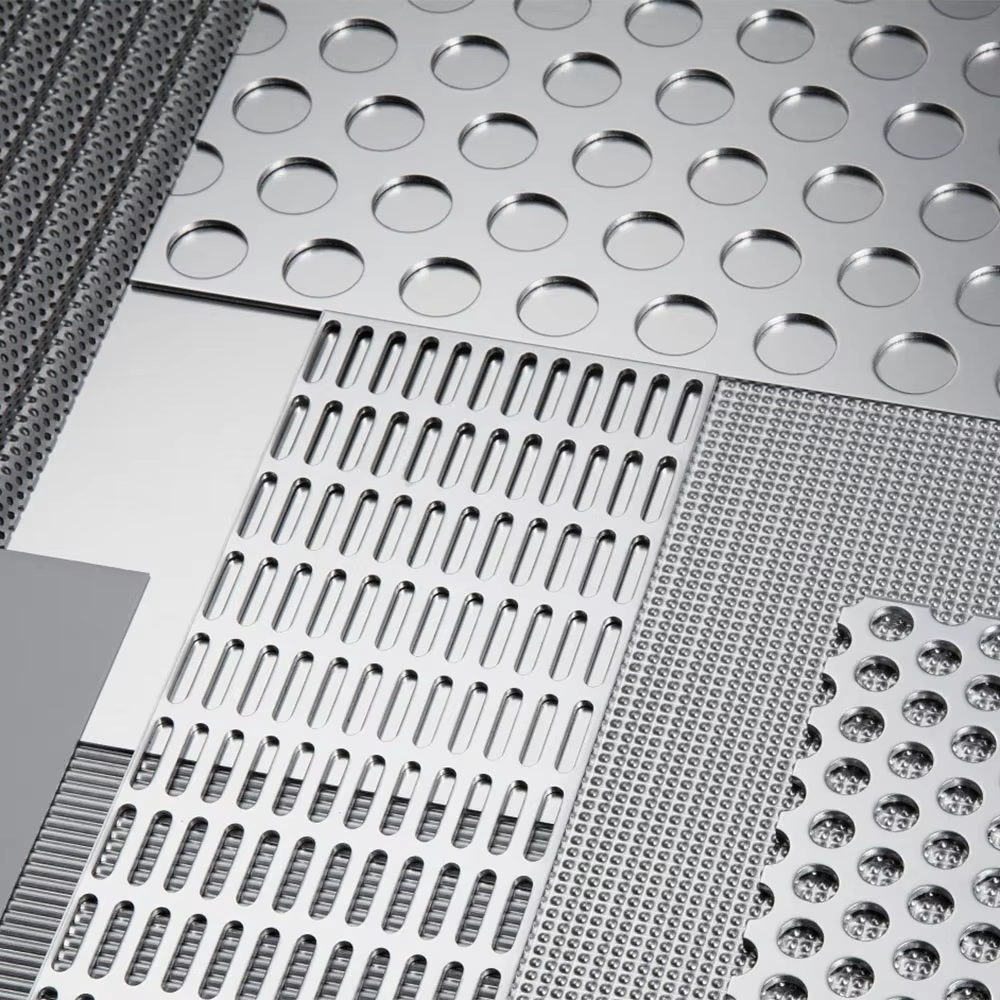
Perforated Metal Sheet is one of the most versatile and stylish metal protects in our life, has various hole sizes, high strength-to-weight ratio, good ventilation and light penetration. It is a metal plate with various shapes of holes on the surface.Product applications are widely used in various industries such as pharmaceutical equipment, food and beverage machinery, harvesting machines, dry cleaning machines,sound elimination equipment, refrigeration equipment (central air conditioning) speakers, and filtering equipment.

Functional Features
2. Versatility: We can be used to process a wide range of materials, including metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
This makes it a versatile choice for many industries that require custom metal parts.
3. Fast Speed and Low-Cost: It can lead to faster turnaround times and lower costs for customers. Additionally, since the process
is automated, it requires minimal manual labor and allowing for more efficient production.
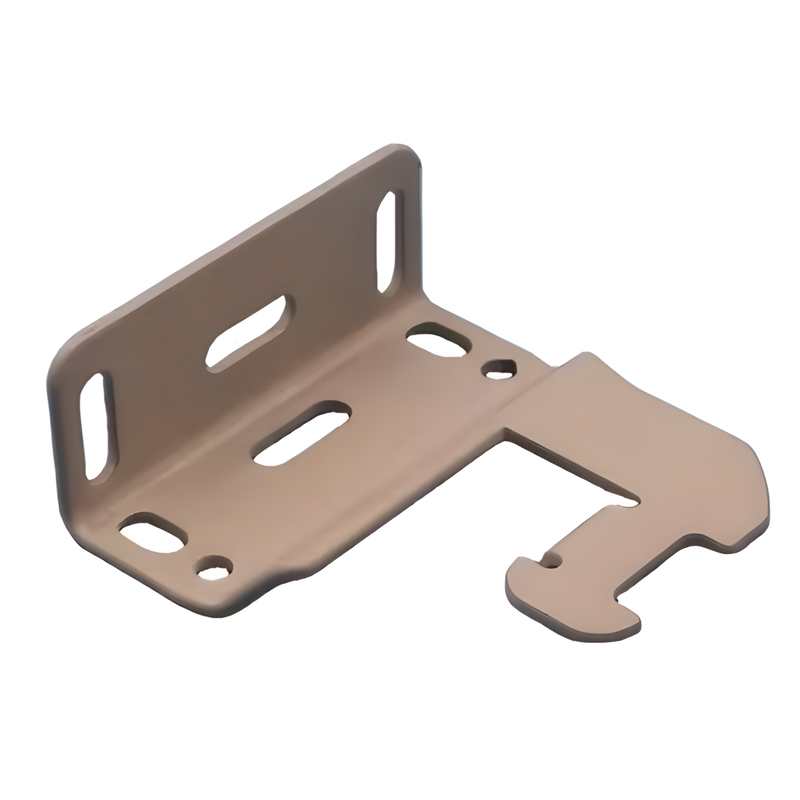
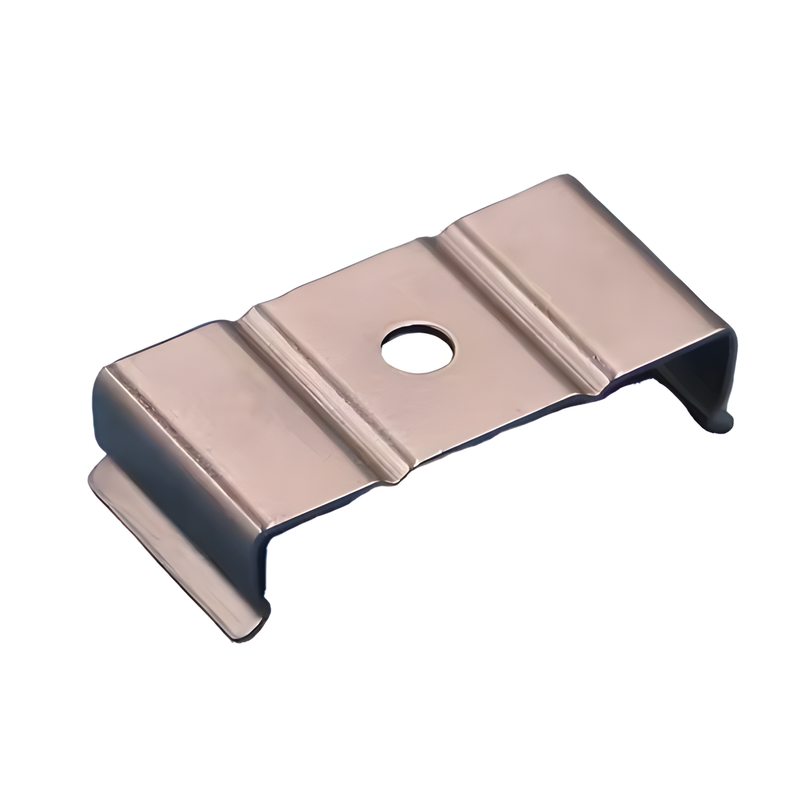
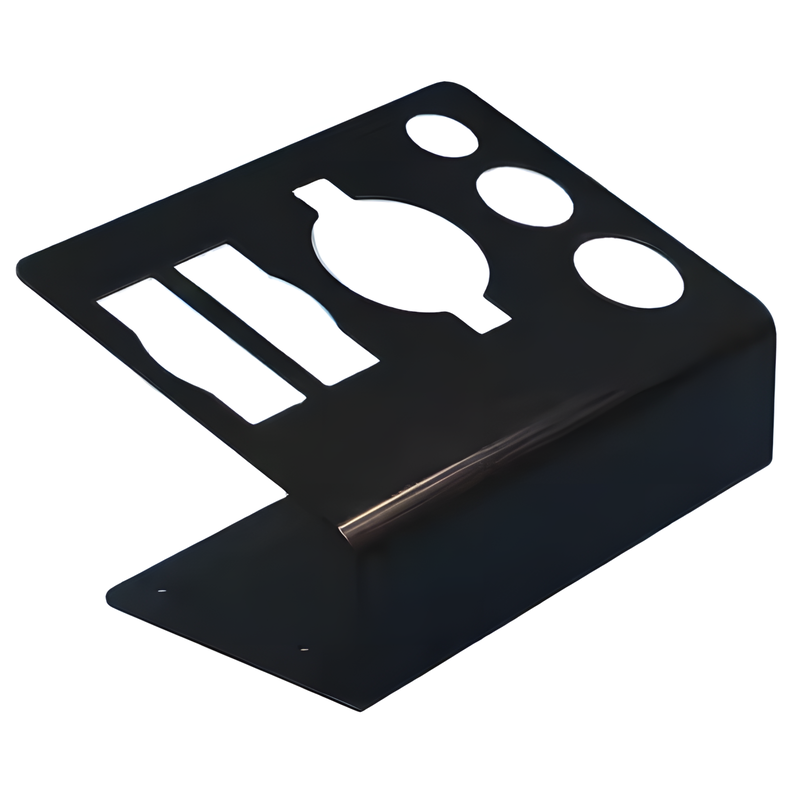
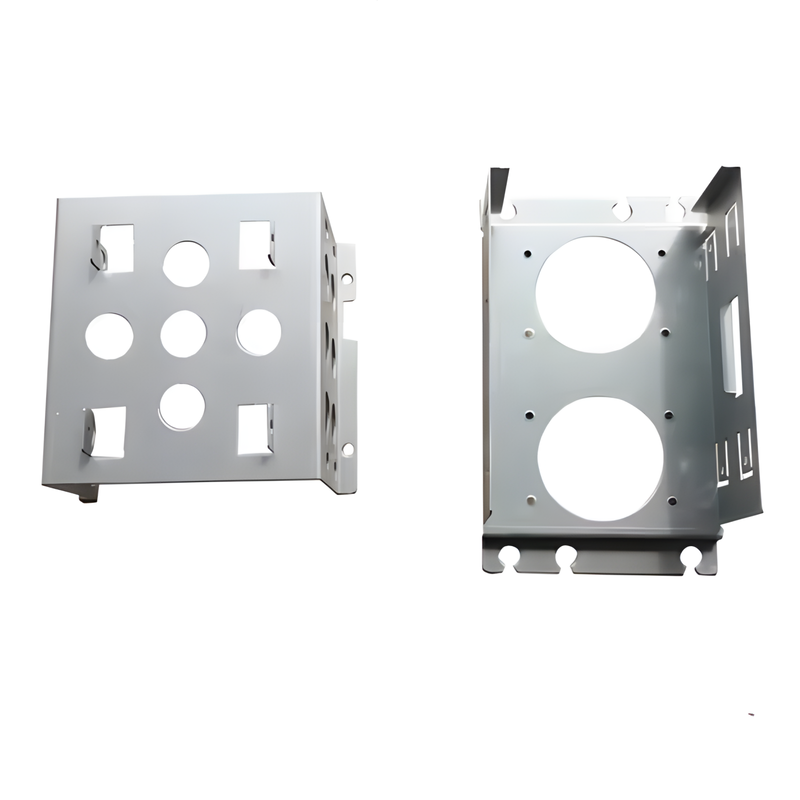
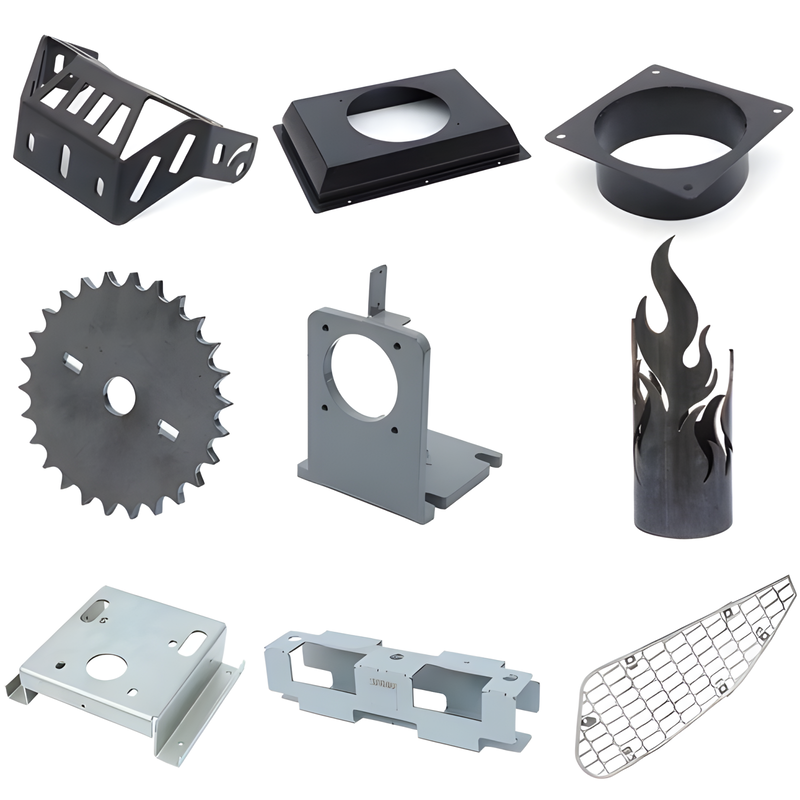
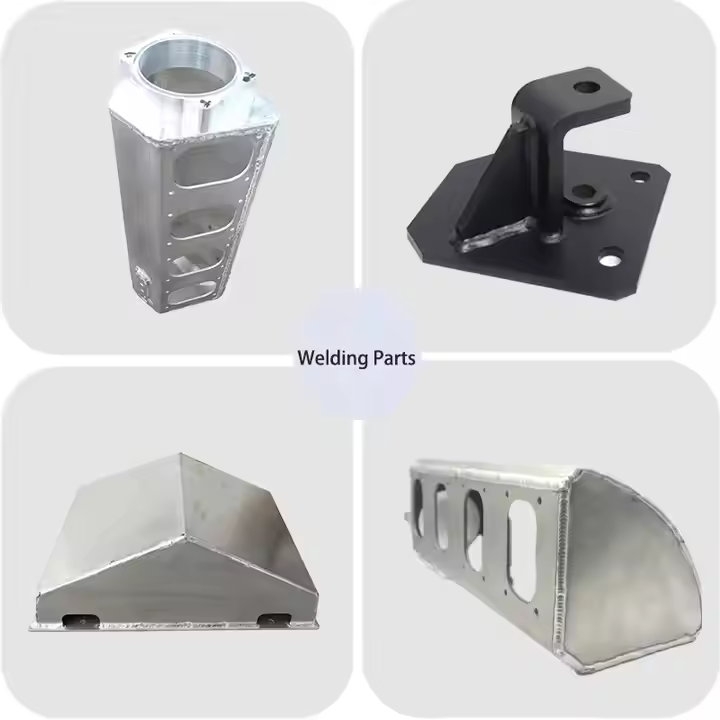
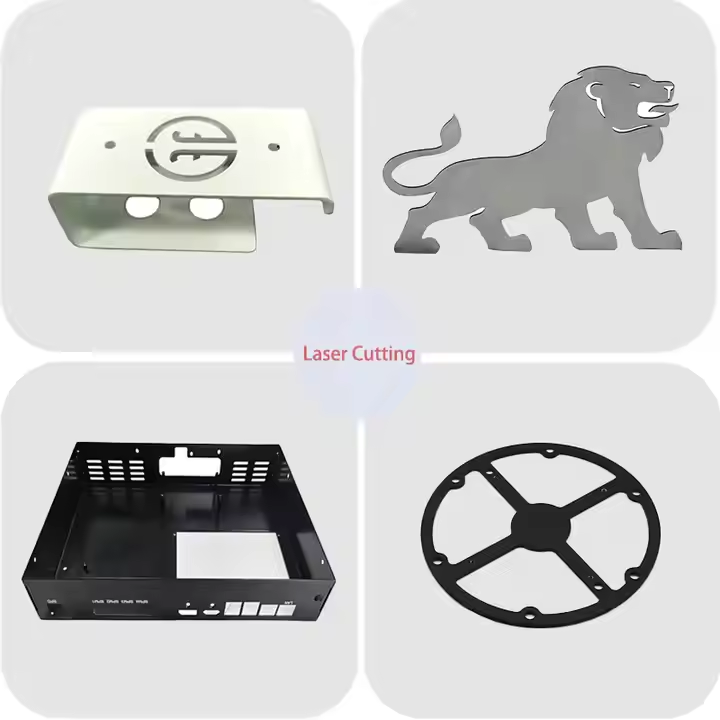
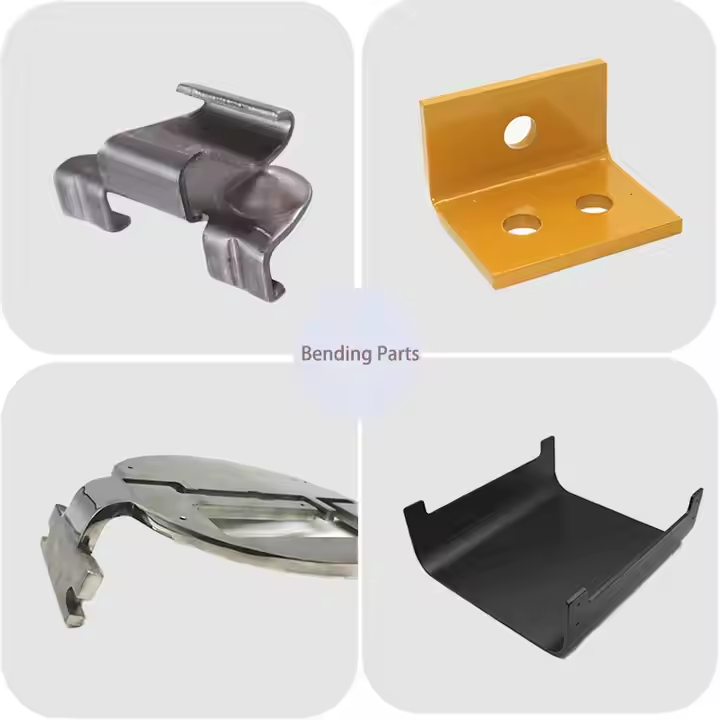
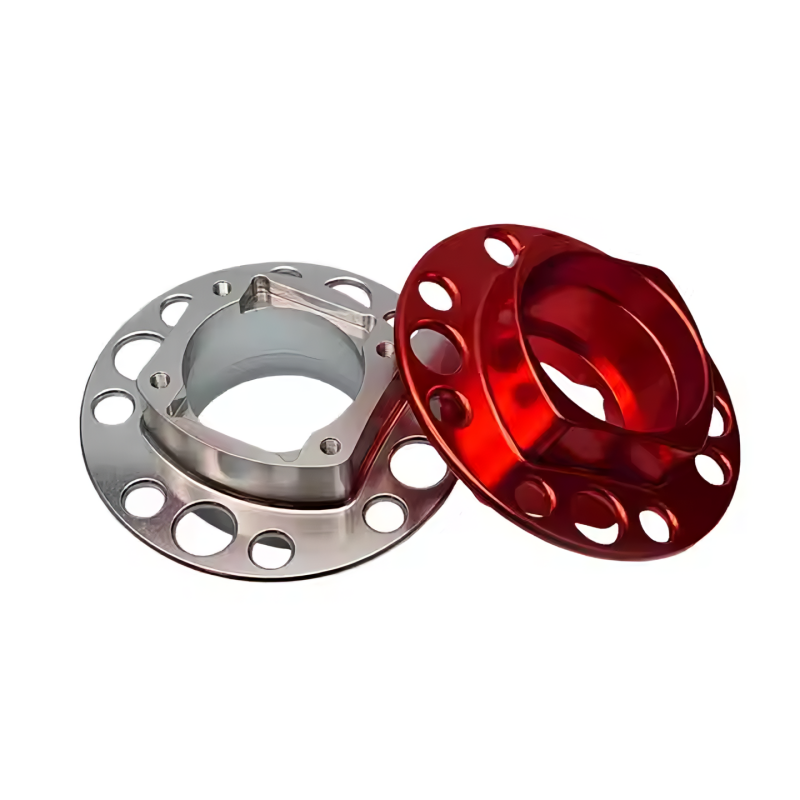
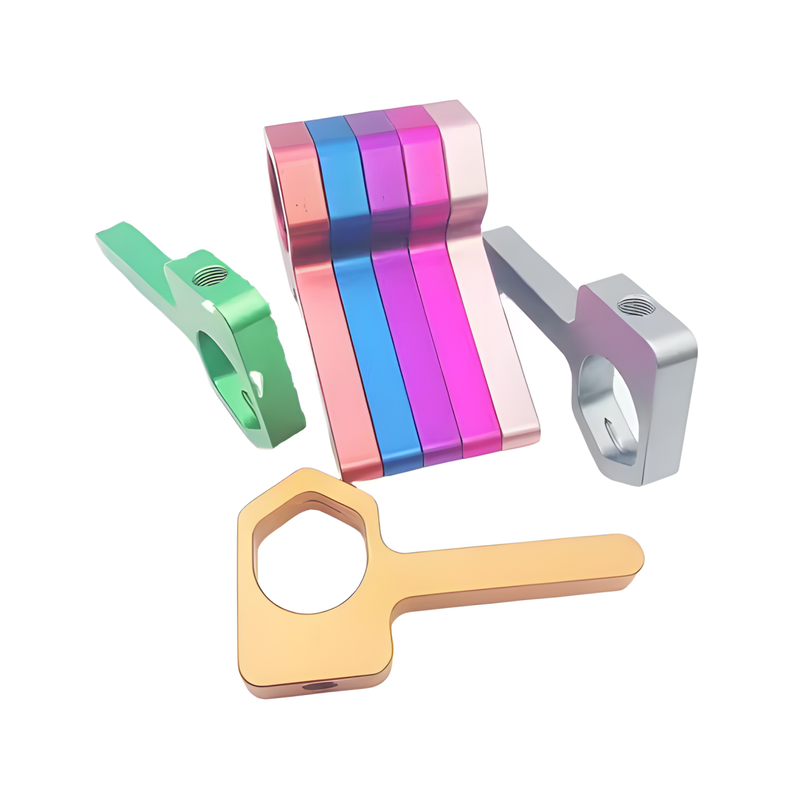
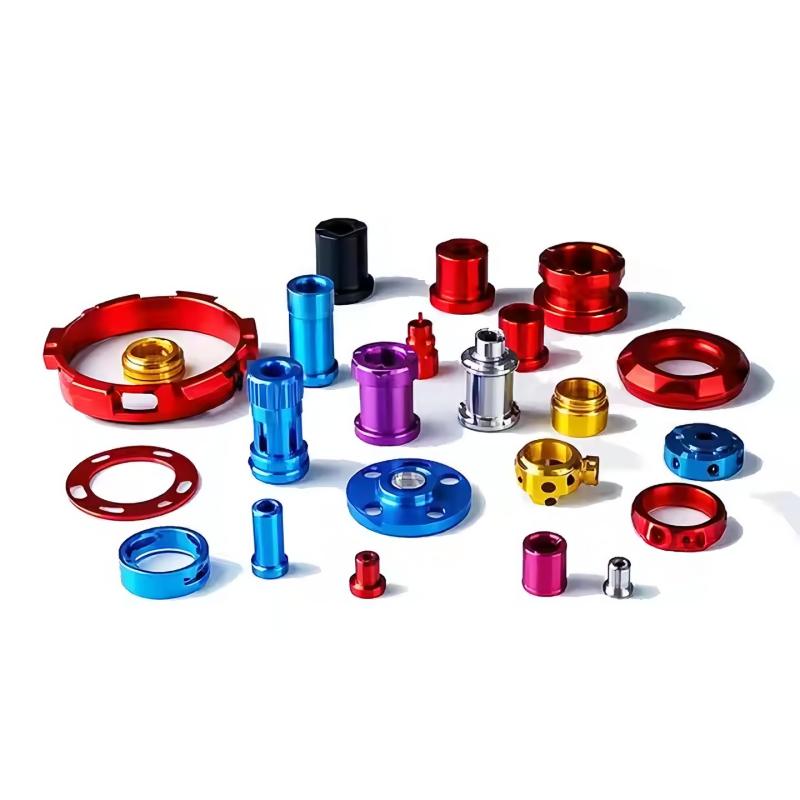
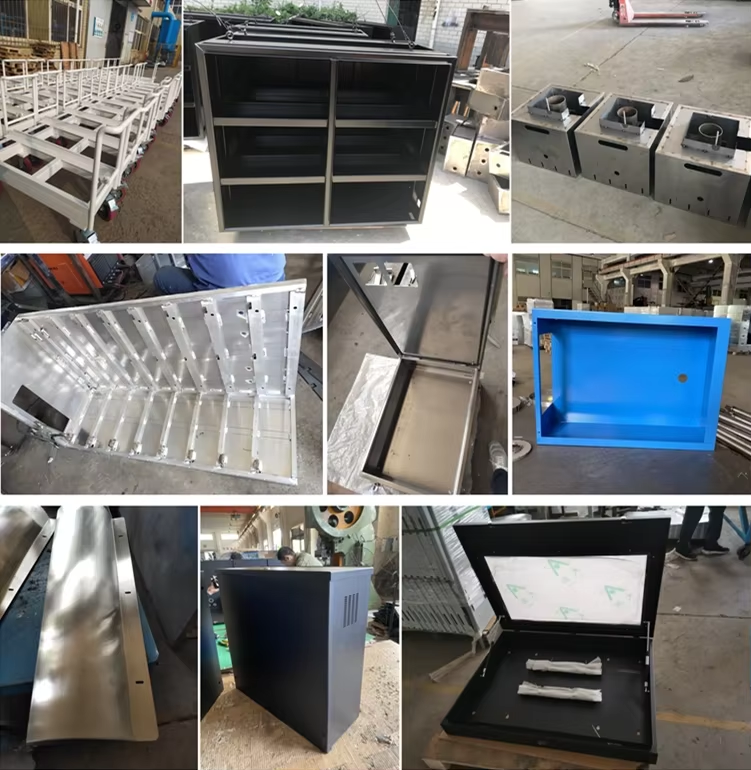
Product Display
|
|
|
|
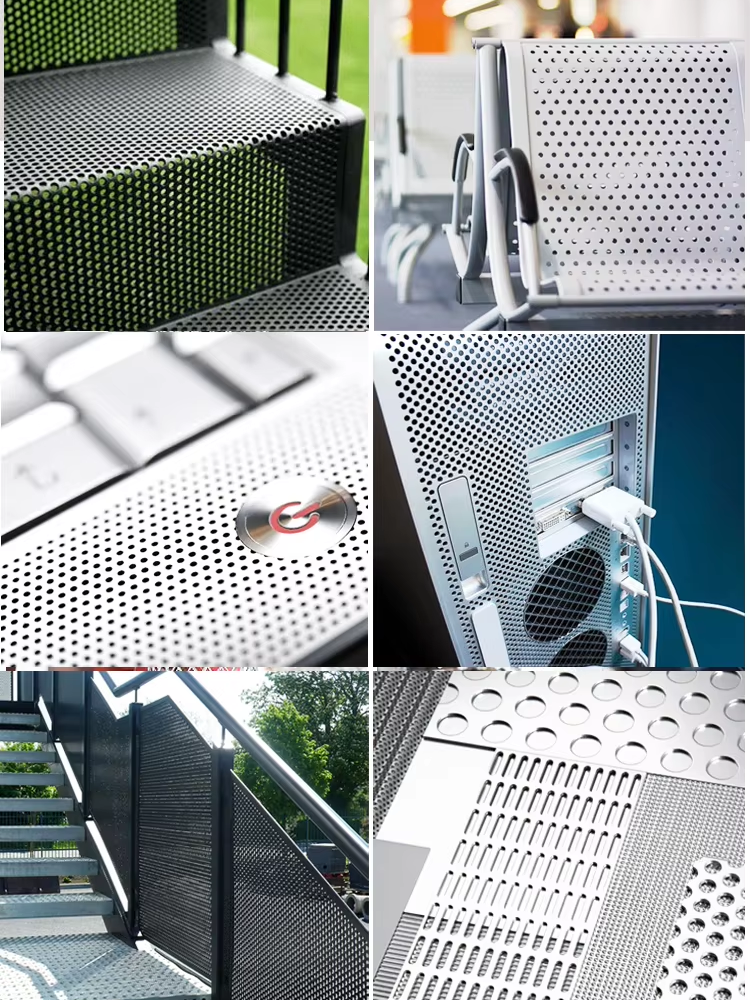
Application
| Electrical Enclosures and Components |
|
| Automotive Parts |
|
| Construction and Architecture |
|
| Consumer Electronics and Appliances |
|
| Industrial Equipment and Hardware |
|
| Medical Devices and Instrumentation |
|
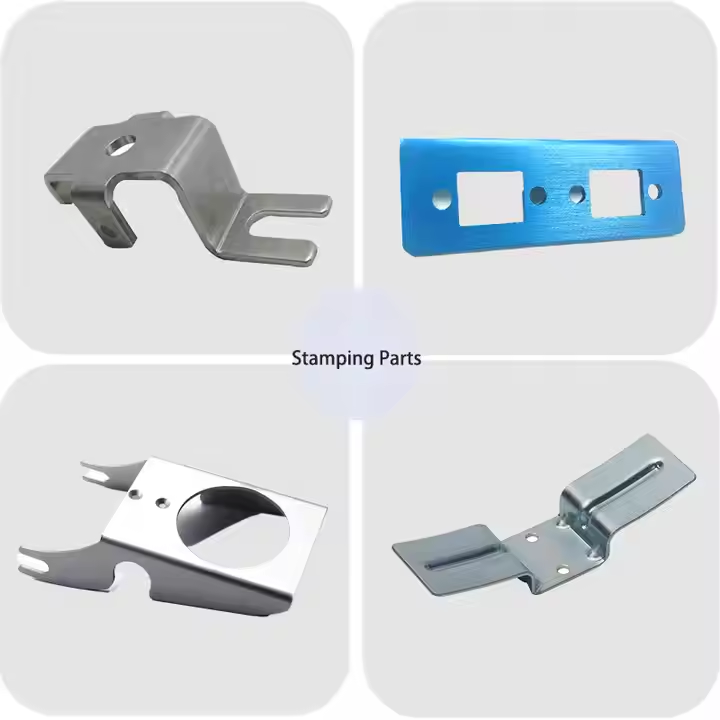
Advantages of Using Stamping for Zinc Sheet Metal
Precision & Repeatability: Ideal for mass production of detailed and consistent parts.
Speed: High-speed stamping presses reduce manufacturing time compared to manual or CNC processes.
Complex Shapes: Multi-stage dies allow forming, bending, punching, and embossing in one cycle.
Cost-Efficiency: Lower per-part cost for medium to high-volume production.
Material Efficiency: Optimized material use with minimal waste in sheet layouts.
Product parameters
Material Properties (Zinc Sheet)
| Thickness | 0.2 mm to 3 mm (common) |
| Hardness | ~50–80 HV (varies with alloy) |
| Tensile Strength | 90–250 MPa (depending on alloy and temper) |
| Elongation | ~10–30% |
| Coating (if galvanized) | Zinc layer ~5–30 µm |
Die and Tooling Parameters
| Die Clearance | Typically 5–10% of material thickness per side (depends on alloy hardness) |
| Punch Radius | Should match bend radius; too sharp causes cracking |
| Die Material | Hardened tool steel or carbide for long life |
| Lubrication | Essential for preventing galling and tool wear; use zinc-compatible lubricants |
Machine Parameters
| Press Tonnage | Depends on part size, thickness, and operation (blanking, bending, etc.) |
| Stroke Speed | Adjusted based on part complexity and material; higher for simple blanking |
| Feed Rate | Depends on press automation; faster for high-volume production |
| Press Type | Mechanical for high-speed, hydraulic for precise/forming operations |
Custom Process

Question

Quotation

Mass Production

Transportation
Quality Control

| Material Thickness | As per drawing ±0.05 mm | Caliper / Micrometer | Per batch / Random lot |
| Hole Diameter | As per drawing ±0.05 mm | Pin Gauge / Caliper | Random sampling |
| Bend Angle | As per drawing ±1° | Protractor / Angle Gauge | First piece & periodic |
| Flatness | Max 0.3 mm deviation across part | Surface Plate + Feeler Gauge | Per batch |
| Surface Defects | No scratches, dents, or stains | Visual Inspection | 100% |
FAQ
1. What is zinc sheet metal stamping?
Zinc stamping is a fabrication process that uses a stamping press and die to form, cut, or shape zinc sheet metal into specific parts or components. It's ideal for high-volume, precision parts with consistent quality.
2. What are the advantages of using zinc for stamped parts?
Excellent corrosion resistance
Good formability and malleability
Suitable for fine detail and tight tolerances
Non-sparking and conductive (useful in electrical applications)
3. What thicknesses of zinc sheet metal can be stamped?
Typically, 0.2 mm to 3 mm thick sheets are used. The exact range depends on the part design and press capacity.
4. What types of stamping operations are used on zinc?
Blanking – cutting flat shapes
Piercing – punching holes
Bending – creating angles or curves
Embossing – raising or recessing surface patterns
Deep drawing – forming into deeper shapes (with some zinc alloys)
5. How is quality controlled in zinc stamping?
Key QC checks include:
Dimensional accuracy
Hole position and diameter
Burr height
Surface defects (cracks, scratches)
Zinc coating integrity (for galvanized materials)
Flatness and fit






















